Industrial aluminum profiles are widely used in various industries due to their lightweight, durability, and versatility. Understanding the different types and grades of aluminum profiles is crucial for selecting the most appropriate option for specific applications. This article provides a comprehensive comparison of industrial aluminum profiles, highlighting their characteristics and applications.
Types of Aluminum Profiles
Solid Aluminum Profiles
Solid profiles are made from a single piece of aluminum, resulting in high strength and durability. They are suitable for applications requiring structural rigidity and impact resistance.
Extruded Aluminum Profiles
– Extruded profiles are formed by forcing molten aluminum through a die to create a specific cross-sectional shape. This process allows for complex and intricate designs. Extruded profiles offer a wide range of strength and weight options.
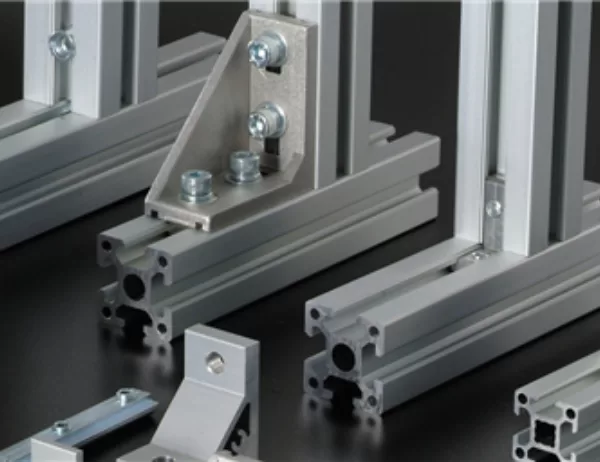
– T-Slot Profiles
– T-slot profiles feature a series of T-shaped slots along their length, enabling easy assembly and customization using T-slot fasteners. They are commonly used in automation, machinery, and other industrial settings.
– U-Channel Profiles
– U-channel profiles have a U-shaped cross-section, making them suitable for applications that require channels or guides. They are used in electrical enclosures, conveyor systems, and construction.
Grades of Aluminum Profiles
6000 Series Aluminum
– 6000 series aluminum profiles are characterized by high strength, good weldability, and corrosion resistance. They are commonly used in structural applications, such as bridges, building frames, and aircraft components.
7000 Series Aluminum
– 7000 series aluminum profiles offer the highest strength-to-weight ratio, making them suitable for aerospace, automotive, and military applications. They have excellent machinability and durability.
Selection Criteria
When selecting industrial aluminum profiles, consider the following factors:
Application Requirements
– Determine the strength, weight, and corrosion resistance required for the intended application.
Fabrication Processes
– Consider the fabrication processes involved, such as welding, cutting, or machining, and choose profiles compatible with the specific processes.
Environmental Conditions
– Consider the environmental conditions in which the profiles will be used and select profiles with adequate corrosion resistance and weatherability.
Cost and Availability
– Evaluate the cost and availability of different profiles and select the option that meets both budgetary and practical requirements.
Industrial aluminum profiles offer a diverse range of options to meet specific application requirements. By understanding the differences in types and grades, engineers and designers can optimize their selection process and choose the most appropriate aluminum profiles for their next project.