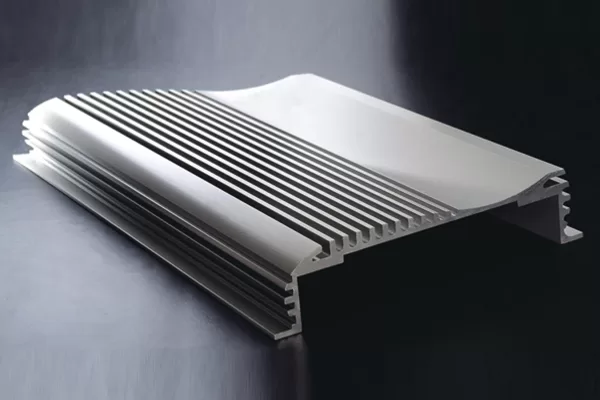
Inverter heat sinks are used to dissipate heat from variable frequency drives (VFDs). VFDs are becoming increasingly popular in a variety of applications, such as industrial machinery, pumps, and fans. By controlling the frequency of the AC power supplied to a motor, VFDs can vary the speed of the motor. This can save energy, improve process control, and reduce noise and vibration.
However, VFDs also generate a significant amount of heat. This heat can damage the VFD’s components and reduce its lifespan. Inverter heat sinks are used to dissipate this heat and keep the VFD operating at a safe temperature.
Benefits of Using Inverter Heat Sinks
There are many benefits to using inverter heat sinks, including:
Improved system performance: Inverter heat sinks can help to improve system performance by reducing the temperature of the VFD. This can lead to increased efficiency, longer component life, and reduced downtime.
Increased energy efficiency: By reducing the temperature of the VFD, inverter heat sinks can help to reduce energy consumption. This can lead to significant savings over the life of the system.
Extended component life: Inverter heat sinks can help to extend the life of the VFD’s components by reducing their operating temperature. This can lead to reduced maintenance costs and less downtime.
Reduced downtime: Inverter heat sinks can help to reduce downtime by preventing the VFD from overheating. This can lead to increased productivity and profitability.
How Inverter Heat Sinks Work
Inverter heat sinks work by transferring heat from the VFD’s components to the surrounding air. The heat is transferred through a process called convection. Convection occurs when a fluid (in this case, air) is heated and rises. As the air rises, it carries heat away from the heat source.
Inverter heat sinks are designed to maximize the surface area available for convection. This allows them to transfer heat more effectively and keep the VFD operating at a lower temperature.
Choosing the Right Inverter Heat Sink
When choosing an inverter heat sink, it is important to consider the following factors:
The size of the VFD: The size of the heat sink will need to be proportional to the size of the VFD.
The power dissipation of the VFD: The power dissipation of the VFD will determine the amount of heat that the heat sink will need to dissipate.
The ambient temperature: The ambient temperature will affect the heat sink’s ability to dissipate heat.
Conclusion
Inverter heat sinks are an important part of any VFD system. By dissipating heat from the VFD’s components, inverter heat sinks can improve system performance, increase energy efficiency, extend component life, and reduce downtime.