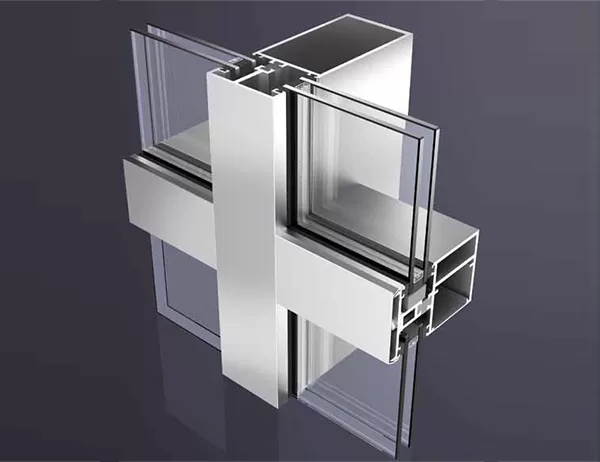
“Technical Insights: Materials and Construction of Aluminum Profiles” delves into the intricacies of aluminum profiles, providing a comprehensive understanding of their composition, manufacturing processes, and properties. This article serves as a valuable resource for architects, engineers, contractors, and anyone seeking to enhance their knowledge of aluminum architectural systems.
Material Composition
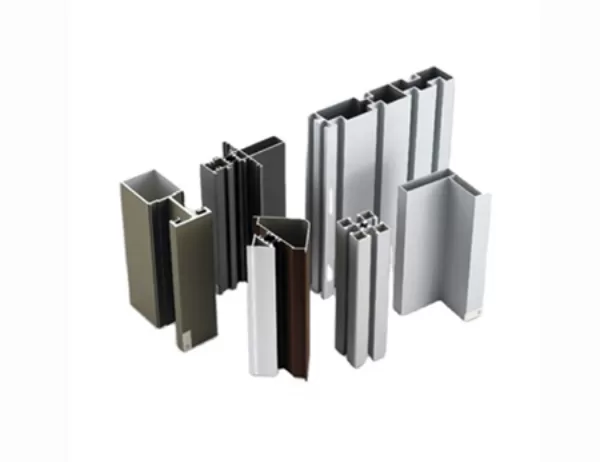
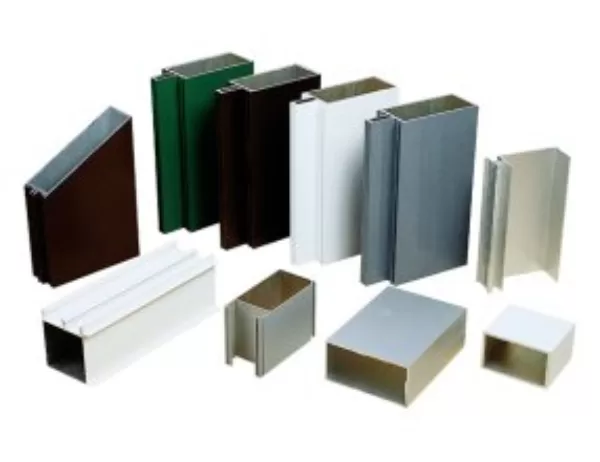
Aluminum profiles are primarily composed of aluminum alloys, which are lightweight, strong, and highly resistant to corrosion. The most commonly used aluminum alloy for profiles is 6063-T5, which offers a good balance of strength, durability, and formability. Other alloys, such as 6061-T6 and 6082-T6, are also employed for specific applications requiring higher strength or corrosion resistance.
Extrusion Process
The extrusion process is the primary method for manufacturing aluminum profiles. Molten aluminum is forced through a die, which shapes the metal into the desired cross-sectional profile. This process allows for the production of complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to produce using other methods.
Surface Treatments
After extrusion, aluminum profiles can undergo various surface treatments to enhance their appearance and performance. Anodizing involves immersing the profile in an electrolytic bath, creating a protective oxide layer that improves corrosion resistance and wear resistance. Powder coating, on the other hand, involves applying a dry powder that is electrostatically charged and baked onto the surface. This provides a durable, colored finish that is resistant to chips and scratches.
Mechanical Properties
Aluminum profiles exhibit exceptional mechanical properties, including high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent stiffness, and resistance to bending and deformation. These properties make them ideal for structural applications such as framing, curtain walls, and window systems. The specific mechanical properties of a profile will vary depending on the alloy composition, temper, and heat treatment.
Thermal Performance
Aluminum profiles have excellent thermal conductivity, which allows them to dissipate heat effectively. This makes them suitable for use in heat exchangers, radiators, and other thermal management applications. The thermal performance of a profile can be further enhanced through the use of thermal breaks, which minimize heat transfer between the interior and exterior of the building.
Durability and Sustainability
Aluminum profiles are known for their exceptional durability, with a lifespan of up to 50 years or more. They are highly resistant to corrosion, weathering, and other environmental factors. Additionally, aluminum is a recyclable material, making it an environmentally friendly option for building and construction.