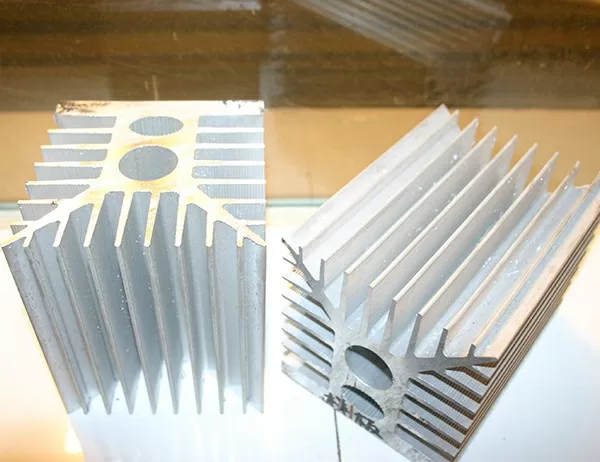
Heat sinks are an essential component in electronics, playing a crucial role in dissipating heat and preventing devices from overheating. Among the various materials used for heat sinks, aluminum and copper are the most common. This article will delve into a comprehensive comparison of aluminum vs. copper heat sinks, examining their performance, cost, and other key aspects to guide your selection.
Thermal conductivity measures a material’s ability to transfer heat. Copper possesses a significantly higher thermal conductivity than aluminum, approximately 401 W/m-K compared to 237 W/m-K. This means that copper heat sinks can conduct heat away from the source more efficiently, resulting in better cooling performance.
Aluminum is a lightweight metal, while copper is denser. Aluminum heat sinks are typically lighter than copper ones of the same size. This difference in weight can be an important factor for applications where weight is a concern, such as in aerospace and portable electronics.
Cost is a major factor to consider when choosing a heat sink material. Aluminum is generally less expensive than copper, making aluminum heat sinks a more economical option. However, the cost difference may vary depending on market fluctuations and the specific size and design of the heat sinks.
Corrosion resistance is crucial in environments where moisture and chemicals are present. Aluminum heat sinks are more susceptible to corrosion than copper ones. Copper heat sinks exhibit superior corrosion resistance, particularly in marine and industrial applications.
Surface treatment can enhance the performance and durability of heat sinks. Anodization is a common surface treatment for aluminum heat sinks, which creates a protective oxide layer that improves corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity. Copper heat sinks can be nickel-plated to provide additional corrosion resistance and a more aesthetically pleasing finish.
The design of a heat sink significantly influences its performance. Aluminum heat sinks can be extruded or CNC machined, allowing for complex shapes and intricate fin designs. Copper heat sinks are typically manufactured through casting or forging, which limits the complexity of their geometry.
Aluminum heat sinks are commonly used in consumer electronics, computers, and power supplies, where cost and weight are primary concerns. Copper heat sinks are found in applications where cooling performance and corrosion resistance are paramount, such as in high-power electronics, automotive engines, and industrial equipment.
Aluminum and copper heat sinks offer unique advantages and disadvantages based on specific applications and requirements. While copper provides superior thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, aluminum is a more economical option with lower weight and design flexibility. Understanding the key differences between these materials will enable you to make an informed decision when selecting a heat sink for your specific application.