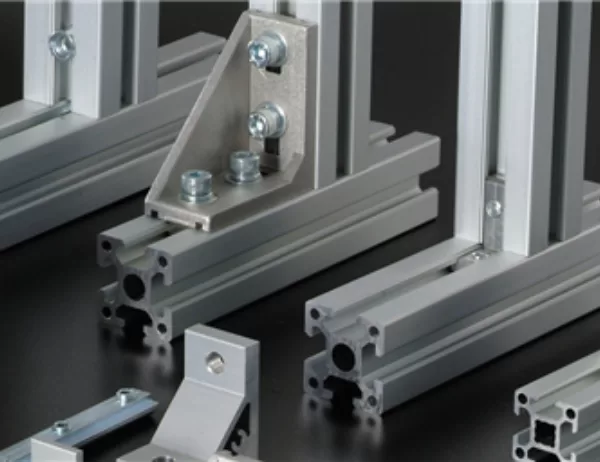
In the realm of industrial manufacturing, aluminum profiles play a pivotal role as structural components and aesthetic enhancements. Selecting the appropriate size and shape for these profiles demands careful consideration, as it directly impacts the performance and functionality of the final product. This article delves into the intricacies of choosing the right size and shape for industrial aluminum profiles, providing valuable insights for engineers and designers.
Factors Influencing Size Selection
1. Load-Bearing Capacity:
The size of the aluminum profile is determined primarily by its intended load-bearing capacity. Factors such as the weight and distribution of the components being supported, as well as the environmental loading conditions, must be taken into account. Larger profiles offer greater strength and rigidity, enabling them to withstand heavier loads.
2. Stiffness and Deflection:
The stiffness of an aluminum profile refers to its resistance to bending under load. A stiffer profile will exhibit less deflection, ensuring precision and stability in critical applications. The thickness and shape of the profile contribute significantly to its stiffness.
Shape Considerations
1. Slotted Profiles:
Slotted profiles feature a series of slots along their length, providing flexibility in mounting and assembly. They are ideal for applications requiring adjustability and modularity, such as machine enclosures and racking systems.
2. Extruded Profiles:
Extruded profiles are created by forcing molten aluminum through a die, resulting in complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy. They offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and can be customized to meet specific design requirements.
3. Tubular Profiles:
Tubular profiles consist of a hollow cylindrical shape, providing stiffness and stability in lightweight structures. They are commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Additional Considerations
1. Material Grade:
The grade of aluminum alloy used in the profile determines its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Higher-grade alloys offer superior properties, making them suitable for demanding applications.
2. Surface Treatments:
Surface treatments, such as anodizing and powder coating, enhance the appearance, durability, and corrosion resistance of aluminum profiles. They provide additional protection against wear, scratching, and environmental factors.
3. Compatibility:
When integrating aluminum profiles into larger systems, compatibility with other components is crucial. Factors such as mounting hardware, connecting elements, and electrical connections must be considered to ensure seamless integration and functionality.
Conclusion
Choosing the right size and shape for industrial aluminum profiles requires a comprehensive understanding of the intended application, load requirements, and design constraints. By considering the factors discussed in this article, engineers and designers can optimize the performance, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of their products. Careful selection ensures the profiles provide the necessary strength, stiffness, and flexibility, while enhancing the overall durability and reliability of the final assembly.