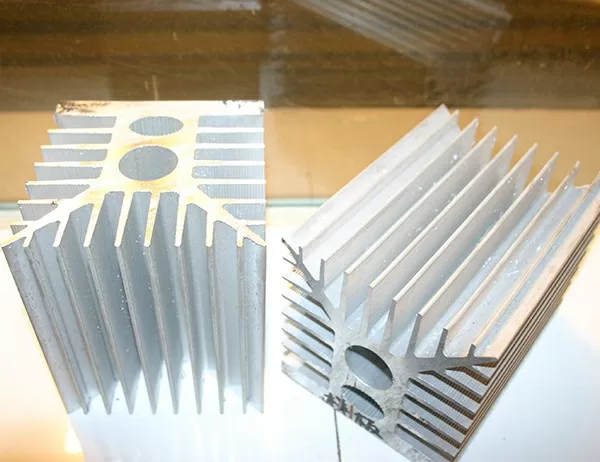
When selecting an inverter heat sink for high-power applications, it is important to consider several factors, including the power dissipation of the inverter, the type of cooling system used, and the available space.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an Inverter Heat Sink
Power Dissipation
The power dissipation of the inverter is a key factor in determining the size and type of heat sink required. The higher the power dissipation, the larger the heat sink that will be needed.
Cooling System
The type of cooling system used will also affect the size and type of heat sink required. Air-cooled heat sinks are typically smaller and less expensive than liquid-cooled heat sinks, but they are also less efficient. Liquid-cooled heat sinks are more efficient, but they are also larger and more expensive.
Available Space
The available space is another important factor to consider when selecting an inverter heat sink. Heat sinks can be made in a variety of shapes and sizes, so it is important to find one that will fit in the available space.
Features of the Best Inverter Heat Sinks
The best inverter heat sinks are designed to maximize heat dissipation and minimize thermal resistance. They are typically made of high-quality materials, such as aluminum or copper, and they have a large surface area to promote heat transfer. Some of the features of the best inverter heat sinks include:
High thermal conductivity: The thermal conductivity of a heat sink is a measure of its ability to transfer heat. The higher the thermal conductivity, the more heat the heat sink can dissipate.
Large surface area: The surface area of a heat sink is a measure of the amount of contact it has with the air or coolant. The larger the surface area, the more heat the heat sink can dissipate.
Low thermal resistance: The thermal resistance of a heat sink is a measure of its resistance to heat flow. The lower the thermal resistance, the more heat the heat sink can dissipate.
Benefits of Using the Best Inverter Heat Sinks
Using the best inverter heat sinks provides several benefits, including:
Reduced thermal stress: Heat sinks help to reduce thermal stress on the inverter by transferring heat away from the inverter’s components. This can help to extend the life of the inverter.
Improved efficiency: By reducing thermal stress, heat sinks can help to improve the efficiency of the inverter. This can lead to lower operating costs.
Increased reliability: Heat sinks can help to increase the reliability of the inverter by preventing it from overheating. This can help to reduce downtime and maintenance costs.